۵-متوکسیتریپتامین
 | |
| شناسهها | |
|---|---|
| |
| شمارهٔ سیایاس | |
| پابکم CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| کماسپایدر | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.231 |
| دادههای فیزیکی و شیمیایی | |
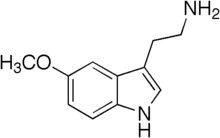
| فرمول شیمیایی | C11H14N2O |
| جرم مولی | ۱۹۰٫۲۴۶ g·mol−1 |
| مدل سه بعدی (جیمول) | |
| |
| |
| (صحتسنجی) | |
۵-متوکسیتریپتامین (انگلیسی: 5-Methoxytryptamine) یکی از مشتقات تریپتامین است که شباهت ساختاری فراوانی به پیامرسان عصبی «سروتونین» و «ملاتونین» دارد. این ماده به مقدار اندک در بدن ساخته میشود[۱] و این کار به دِاستیله شدنِ هورمون ملاتونین در غده کاجی رخ میدهد.[۱]
۵-متوکسیتریپتامین آگونیست گیرنده ۱ سروتونین، گیرنده ۲ سروتونین، گیرنده ۴ سروتونین، گیرنده ۶ سروتونین و گیرنده ۷ سروتونین است،[۲][۳][۴][۵][۶][۷][۸] اما هیچگونه میل ترکیبی به گیرنده ۳ سروتونین ندارد و میل ترکیبیاش به گیرنده ۱ ئی سروتونین بسیار ضعیف است.[۵][۹] هنوز معلوم نیست تمایل این ماده شیمیایی به گیرنده ۵ آ سروتونین تا چه حد است.
جستارهای وابسته[ویرایش]
منابع[ویرایش]
- ↑ ۱٫۰ ۱٫۱ Galzin AM, Eon MT, Esnaud H, Lee CR, Pévet P, Langer SZ (1988). "Day-night rhythm of 5-methoxytryptamine biosynthesis in the pineal gland of the golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus)". J. Endocrinol. 118 (3): 389–397. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1180389. PMID 2460575.
- ↑ Wu PH, Gurevich N, Carlen PL (1988). "Serotonin-1A receptor activation in hippocampal CA1 neurons by 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, 5-methoxytryptamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine". Neurosci. Lett. 86 (1): 72–76. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(88)90185-1. PMID 2966313. S2CID 21620262.
- ↑ Yamada J, Sugimoto Y, Yoshikawa T, Horisaka K (1997). "Hyperglycemia induced by the 5-HT receptor agonist, 5-methoxytryptamine, in rats: involvement of the peripheral 5-HT2A receptor". Eur J Pharmacol. 323 (2–3): 235–240. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(97)00029-0. PMID 9128844.
- ↑ Amemiya N, Hatta S, Takemura H, Ohshika H (1996). "Characterization of the contractile response induced by 5-methoxytryptamine in rat stomach fundus strips". Eur J Pharmacol. 318 (2–3): 403–409. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00777-7. PMID 9016931.
- ↑ ۵٫۰ ۵٫۱ Craig DA, Eglen RM, Walsh LK, Perkins LA, Whiting RL, Clarke DE (1990). "5-Methoxytryptamine and 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine-induced desensitization as a discriminative tool for the 5-HT3 and putative 5-HT4 receptors in guinea pig ileum". Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 342 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1007/bf00178965. PMID 2402303. S2CID 24743785.
- ↑ Boess FG, Monsma Jr FJ, Carolo C, Meyer V, Rudler A, Zwingelstein C, Sleight AJ (1997). "Functional and radioligand binding characterization of rat 5-HT6 receptors stably expressed in HEK293 cells". Neuropharmacology. 36 (4–5): 713–720. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(97)00019-1. PMID 9225298. S2CID 41813873.
- ↑ Hemedah M, Coupar IM, Mitchelson FJ (1999). "[3H]-Mesulergine labels 5-HT7 sites in rat brain and guinea-pig ileum but not rat jejunum". Br J Pharmacol. 126 (1): 179–188. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702293. PMC 1565797. PMID 10051134.
- ↑ Glennon RA, Dukat M, Westkaemper RB (2000-01-01). "Serotonin Receptor Subtypes and Ligands". American College of Neurophyscopharmacology. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- ↑ Roth, Brian (2006). The serotonin receptors. Humana Press. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-58829-568-2.
- مشارکتکنندگان ویکیپدیا. «5-Methoxytryptamine». در دانشنامهٔ ویکیپدیای انگلیسی، بازبینیشده در ۵ نوامبر ۲۰۲۰.
