پی۵۳: تفاوت میان نسخهها
Fatranslator (بحث | مشارکتها) جز ربات:افزودن الگو ناوباکس {{عوامل رونویسی و گیرندههای درونسلولی}}+ |
←لید: بازنویسی متن لید |
||
| خط ۲: | خط ۲: | ||
| Name = پروتئین تومور پی۵۳ |
| Name = پروتئین تومور پی۵۳ |
||
| image = p53.png |
| image = p53.png |
||
| image_source = [[بانک داده پروتئین]] |
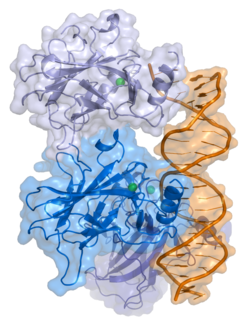
| image_source = [[بانک داده پروتئین]]: P53 کمپلکس همراه DNA<ref name="pmid 8023157">{{cite journal | author = Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP | title = Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations | journal = Science | volume = 265 | issue = 5170 | pages = 346–55 | year = 1994 | pmid = 8023157 | doi = 10.1126/science.8023157}}</ref> |
||
| PDB = {{PDB2|1A1U}}, {{PDB2|1AIE}}, {{PDB2|1C26}}, {{PDB2|1DT7}}, {{PDB2|1GZH}}, {{PDB2|1H26}}, {{PDB2|1HS5}}, {{PDB2|1JSP}}, {{PDB2|1KZY}}, {{PDB2|1MA3}}, {{PDB2|1OLG}}, {{PDB2|1OLH}}, {{PDB2|1PES}}, {{PDB2|1PET}}, {{PDB2|1SAE}}, {{PDB2|1SAF}}, {{PDB2|1SAK}}, {{PDB2|1SAL}}, {{PDB2|1TSR}}, {{PDB2|1TUP}}, {{PDB2|1UOL}}, {{PDB2|1XQH}}, {{PDB2|1YC5}}, {{PDB2|1YCQ}}, {{PDB2|1YCR}}, {{PDB2|1YCS}}, {{PDB2|2AC0}}, {{PDB2|2ADY}}, {{PDB2|2AHI}}, {{PDB2|2ATA}}, {{PDB2|2B3G}}, {{PDB2|2BIM}}, {{PDB2|2BIN}}, {{PDB2|2BIO}}, {{PDB2|2BIP}}, {{PDB2|2BIQ}}, {{PDB2|2F1X}}, {{PDB2|2FEJ}}, {{PDB2|2FOJ}}, {{PDB2|2FOO}}, {{PDB2|2GS0}}, {{PDB2|2H1L}}, {{PDB2|2H2D}}, {{PDB2|2H2F}}, {{PDB2|2H4F}}, {{PDB2|2H4H}}, {{PDB2|2H4J}}, {{PDB2|2H59}}, {{PDB2|2J0Z}}, {{PDB2|2J10}}, {{PDB2|2J11}}, {{PDB2|2J1W}}, {{PDB2|2J1X}}, {{PDB2|2J1Y}}, {{PDB2|2J1Z}}, {{PDB2|2J20}}, {{PDB2|2J21}}, {{PDB2|2K8F}}, {{PDB2|2L14}}, {{PDB2|2LY4}}, {{PDB2|2MEJ}}, {{PDB2|2OCJ}}, {{PDB2|2PCX}}, {{PDB2|2VUK}}, {{PDB2|2WGX}}, {{PDB2|2X0U}}, {{PDB2|2X0V}}, {{PDB2|2X0W}}, {{PDB2|2XWR}}, {{PDB2|2YBG}}, {{PDB2|2YDR}}, {{PDB2|2Z5S}}, {{PDB2|2Z5T}}, {{PDB2|3D05}}, {{PDB2|3D06}}, {{PDB2|3D07}}, {{PDB2|3D08}}, {{PDB2|3D09}}, {{PDB2|3D0A}}, {{PDB2|3DAB}}, {{PDB2|3DAC}}, {{PDB2|3IGK}}, {{PDB2|3IGL}}, {{PDB2|3KMD}}, {{PDB2|3KZ8}}, {{PDB2|3LW1}}, {{PDB2|3OQ5}}, {{PDB2|3PDH}}, {{PDB2|3Q01}}, {{PDB2|3Q05}}, {{PDB2|3Q06}}, {{PDB2|3SAK}}, {{PDB2|3TG5}}, {{PDB2|3TS8}}, {{PDB2|3ZME}}, {{PDB2|4AGL}}, {{PDB2|4AGM}}, {{PDB2|4AGN}}, {{PDB2|4AGO}}, {{PDB2|4AGP}}, {{PDB2|4AGQ}}, {{PDB2|4BUZ}}, {{PDB2|4BV2}}, {{PDB2|4HFZ}}, {{PDB2|4HJE}}, {{PDB2|4IBQ}}, {{PDB2|4IBS}}, {{PDB2|4IBT}}, {{PDB2|4IBU}}, {{PDB2|4IBV}}, {{PDB2|4IBW}}, {{PDB2|4IBY}}, {{PDB2|4IBZ}}, {{PDB2|4IJT}}, {{PDB2|4KVP}}, {{PDB2|4LO9}}, {{PDB2|4LOE}}, {{PDB2|4LOF}}, {{PDB2|4MZI}}, {{PDB2|4MZR}} |
| PDB = {{PDB2|1A1U}}, {{PDB2|1AIE}}, {{PDB2|1C26}}, {{PDB2|1DT7}}, {{PDB2|1GZH}}, {{PDB2|1H26}}, {{PDB2|1HS5}}, {{PDB2|1JSP}}, {{PDB2|1KZY}}, {{PDB2|1MA3}}, {{PDB2|1OLG}}, {{PDB2|1OLH}}, {{PDB2|1PES}}, {{PDB2|1PET}}, {{PDB2|1SAE}}, {{PDB2|1SAF}}, {{PDB2|1SAK}}, {{PDB2|1SAL}}, {{PDB2|1TSR}}, {{PDB2|1TUP}}, {{PDB2|1UOL}}, {{PDB2|1XQH}}, {{PDB2|1YC5}}, {{PDB2|1YCQ}}, {{PDB2|1YCR}}, {{PDB2|1YCS}}, {{PDB2|2AC0}}, {{PDB2|2ADY}}, {{PDB2|2AHI}}, {{PDB2|2ATA}}, {{PDB2|2B3G}}, {{PDB2|2BIM}}, {{PDB2|2BIN}}, {{PDB2|2BIO}}, {{PDB2|2BIP}}, {{PDB2|2BIQ}}, {{PDB2|2F1X}}, {{PDB2|2FEJ}}, {{PDB2|2FOJ}}, {{PDB2|2FOO}}, {{PDB2|2GS0}}, {{PDB2|2H1L}}, {{PDB2|2H2D}}, {{PDB2|2H2F}}, {{PDB2|2H4F}}, {{PDB2|2H4H}}, {{PDB2|2H4J}}, {{PDB2|2H59}}, {{PDB2|2J0Z}}, {{PDB2|2J10}}, {{PDB2|2J11}}, {{PDB2|2J1W}}, {{PDB2|2J1X}}, {{PDB2|2J1Y}}, {{PDB2|2J1Z}}, {{PDB2|2J20}}, {{PDB2|2J21}}, {{PDB2|2K8F}}, {{PDB2|2L14}}, {{PDB2|2LY4}}, {{PDB2|2MEJ}}, {{PDB2|2OCJ}}, {{PDB2|2PCX}}, {{PDB2|2VUK}}, {{PDB2|2WGX}}, {{PDB2|2X0U}}, {{PDB2|2X0V}}, {{PDB2|2X0W}}, {{PDB2|2XWR}}, {{PDB2|2YBG}}, {{PDB2|2YDR}}, {{PDB2|2Z5S}}, {{PDB2|2Z5T}}, {{PDB2|3D05}}, {{PDB2|3D06}}, {{PDB2|3D07}}, {{PDB2|3D08}}, {{PDB2|3D09}}, {{PDB2|3D0A}}, {{PDB2|3DAB}}, {{PDB2|3DAC}}, {{PDB2|3IGK}}, {{PDB2|3IGL}}, {{PDB2|3KMD}}, {{PDB2|3KZ8}}, {{PDB2|3LW1}}, {{PDB2|3OQ5}}, {{PDB2|3PDH}}, {{PDB2|3Q01}}, {{PDB2|3Q05}}, {{PDB2|3Q06}}, {{PDB2|3SAK}}, {{PDB2|3TG5}}, {{PDB2|3TS8}}, {{PDB2|3ZME}}, {{PDB2|4AGL}}, {{PDB2|4AGM}}, {{PDB2|4AGN}}, {{PDB2|4AGO}}, {{PDB2|4AGP}}, {{PDB2|4AGQ}}, {{PDB2|4BUZ}}, {{PDB2|4BV2}}, {{PDB2|4HFZ}}, {{PDB2|4HJE}}, {{PDB2|4IBQ}}, {{PDB2|4IBS}}, {{PDB2|4IBT}}, {{PDB2|4IBU}}, {{PDB2|4IBV}}, {{PDB2|4IBW}}, {{PDB2|4IBY}}, {{PDB2|4IBZ}}, {{PDB2|4IJT}}, {{PDB2|4KVP}}, {{PDB2|4LO9}}, {{PDB2|4LOE}}, {{PDB2|4LOF}}, {{PDB2|4MZI}}, {{PDB2|4MZR}} |
||
| HGNCid = |
| HGNCid = ۱۱۹۹۸ |
||
| MGIid = |
| MGIid = ۹۸۸۳۴ |
||
| Symbol = TP53 |
| Symbol = TP53 |
||
| AltSymbols =; BCC7; LFS1; P53; TRP53 |
| AltSymbols =; BCC7; LFS1; P53; TRP53 |
||
| IUPHAR = |
| IUPHAR = |
||
| ChEMBL = |
| ChEMBL = ۴۰۹۶ |
||
| OMIM = |
| OMIM = ۱۹۱۱۷۰ |
||
| ECnumber = |
| ECnumber = |
||
| Homologene = |
| Homologene = ۴۶۰ |
||
| GeneAtlas_image1 = PBB GE TP53 201746 at.png |
| GeneAtlas_image1 = PBB GE TP53 201746 at.png |
||
| GeneAtlas_image2 = PBB GE TP53 211300 s at.png |
| GeneAtlas_image2 = PBB GE TP53 211300 s at.png |
||
| GeneAtlas_image3 = |
| GeneAtlas_image3 = |
||
| Protein_domain_image = |
| Protein_domain_image = |
||
| Function = {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000979 |text = RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001077 |text = RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity involved in positive regulation of transcription}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001085 |text = RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001228 |text = RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity involved in positive regulation of transcription}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002020 |text = protease binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002039 |text = p53 binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003677 |text = DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003682 |text = chromatin binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003684 |text = damaged DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003700 |text = sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005507 |text = copper ion binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005515 |text = protein binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005524 |text = ATP binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008134 |text = transcription factor binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008270 |text = zinc ion binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0019899 |text = enzyme binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0019901 |text = protein kinase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0019903 |text = protein phosphatase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030971 |text = receptor tyrosine kinase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031625 |text = ubiquitin protein ligase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035033 |text = histone deacetylase regulator activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035035 |text = histone acetyltransferase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042802 |text = identical protein binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0044212 |text = transcription regulatory region DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0046982 |text = protein heterodimerization activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0047485 |text = protein N-terminus binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051087 |text = chaperone binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051721 |text = protein phosphatase 2A binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0097371 |text = MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding}} |
| Function = {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000979 |text = RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001077 |text = RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity involved in positive regulation of transcription}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001085 |text = RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001228 |text = RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity involved in positive regulation of transcription}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002020 |text = protease binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002039 |text = p53 binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003677 |text = DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003682 |text = chromatin binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003684 |text = damaged DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0003700 |text = sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005507 |text = copper ion binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005515 |text = protein binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005524 |text = ATP binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008134 |text = transcription factor binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008270 |text = zinc ion binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0019899 |text = enzyme binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0019901 |text = protein kinase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0019903 |text = protein phosphatase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030971 |text = receptor tyrosine kinase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031625 |text = ubiquitin protein ligase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035033 |text = histone deacetylase regulator activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035035 |text = histone acetyltransferase binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042802 |text = identical protein binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0044212 |text = transcription regulatory region DNA binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0046982 |text = protein heterodimerization activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0047485 |text = protein N-terminus binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051087 |text = chaperone binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051721 |text = protein phosphatase 2A binding}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0097371 |text = MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding}} |
||
| Component = {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000785 |text = chromatin}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000790 |text = nuclear chromatin}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005634 |text = nucleus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005654 |text = nucleoplasm}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005657 |text = replication fork}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005669 |text = transcription factor TFIID complex}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005730 |text = nucleolus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005737 |text = cytoplasm}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005739 |text = mitochondrion}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005759 |text = mitochondrial matrix}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005783 |text = endoplasmic reticulum}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005829 |text = cytosol}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016363 |text = nuclear matrix}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016604 |text = nuclear body}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016605 |text = PML body}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043234 |text = protein complex}} |
| Component = {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000785 |text = chromatin}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000790 |text = nuclear chromatin}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005634 |text = nucleus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005654 |text = nucleoplasm}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005657 |text = replication fork}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005669 |text = transcription factor TFIID complex}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005730 |text = nucleolus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005737 |text = cytoplasm}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005739 |text = mitochondrion}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005759 |text = mitochondrial matrix}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005783 |text = endoplasmic reticulum}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0005829 |text = cytosol}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016363 |text = nuclear matrix}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016604 |text = nuclear body}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016605 |text = PML body}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043234 |text = protein complex}} |
||
| Process = {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000060 |text = protein import into nucleus, translocation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000122 |text = negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000733 |text = DNA strand renaturation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001701 |text = in utero embryonic development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001756 |text = somitogenesis}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001836 |text = release of cytochrome c from mitochondria}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002309 |text = T cell proliferation involved in immune response}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002326 |text = B cell lineage commitment}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002360 |text = T cell lineage commitment}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002931 |text = response to ischemia}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006284 |text = base-excision repair}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006289 |text = nucleotide-excision repair}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006302 |text = double-strand break repair}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006355 |text = regulation of transcription, DNA-templated}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006461 |text = protein complex assembly}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006915 |text = apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006974 |text = cellular response to DNA damage stimulus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006977 |text = DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006978 |text = DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006983 |text = ER overload response}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007050 |text = cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007179 |text = transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007219 |text = Notch signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007265 |text = Ras protein signal transduction}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007275 |text = multicellular organismal development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007369 |text = gastrulation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007406 |text = negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007417 |text = central nervous system development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007569 |text = cell aging}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007596 |text = blood coagulation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008104 |text = protein localization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008156 |text = negative regulation of DNA replication}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008283 |text = cell proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008285 |text = negative regulation of cell proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008340 |text = determination of adult lifespan}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0009303 |text = rRNA transcription}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0009651 |text = response to salt stress}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0010165 |text = response to X-ray}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0010332 |text = response to gamma radiation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0010666 |text = positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016032 |text = viral process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030154 |text = cell differentiation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030308 |text = negative regulation of cell growth}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030330 |text = DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030512 |text = negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031065 |text = positive regulation of histone deacetylation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031497 |text = chromatin assembly}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031571 |text = mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0032461 |text = positive regulation of protein oligomerization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0033077 |text = T cell differentiation in thymus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0034103 |text = regulation of tissue remodeling}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0034613 |text = cellular protein localization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0034644 |text = cellular response to UV}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035264 |text = multicellular organism growth}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035690 |text = cellular response to drug}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042149 |text = cellular response to glucose starvation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042771 |text = intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042981 |text = regulation of apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043065 |text = positive regulation of apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043066 |text = negative regulation of apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043525 |text = positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0045892 |text = negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0045893 |text = positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0045944 |text = positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0046677 |text = response to antibiotic}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0046902 |text = regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0048147 |text = negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0048568 |text = embryonic organ development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0050731 |text = positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051097 |text = negative regulation of helicase activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051262 |text = protein tetramerization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051402 |text = neuron apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0070245 |text = positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071158 |text = positive regulation of cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071456 |text = cellular response to hypoxia}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071479 |text = cellular response to ionizing radiation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071850 |text = mitotic cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0072332 |text = intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090200 |text = positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090343 |text = positive regulation of cell aging}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090399 |text = replicative senescence}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090403 |text = oxidative stress-induced premature senescence}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0097193 |text = intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0097252 |text = oligodendrocyte apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:1900740 |text = positive regulation of protein insertion into mitochondrial membrane involved in apoptotic signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:1901525 |text = negative regulation of macromitophagy}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:1902108 |text = regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:2000378 |text = negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:2000379 |text = positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:2001244 |text = positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway}} |
| Process = {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000060 |text = protein import into nucleus, translocation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000122 |text = negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0000733 |text = DNA strand renaturation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001701 |text = in utero embryonic development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001756 |text = somitogenesis}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0001836 |text = release of cytochrome c from mitochondria}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002309 |text = T cell proliferation involved in immune response}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002326 |text = B cell lineage commitment}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002360 |text = T cell lineage commitment}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0002931 |text = response to ischemia}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006284 |text = base-excision repair}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006289 |text = nucleotide-excision repair}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006302 |text = double-strand break repair}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006355 |text = regulation of transcription, DNA-templated}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006461 |text = protein complex assembly}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006915 |text = apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006974 |text = cellular response to DNA damage stimulus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006977 |text = DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006978 |text = DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0006983 |text = ER overload response}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007050 |text = cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007179 |text = transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007219 |text = Notch signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007265 |text = Ras protein signal transduction}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007275 |text = multicellular organismal development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007369 |text = gastrulation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007406 |text = negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007417 |text = central nervous system development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007569 |text = cell aging}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0007596 |text = blood coagulation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008104 |text = protein localization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008156 |text = negative regulation of DNA replication}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008283 |text = cell proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008285 |text = negative regulation of cell proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0008340 |text = determination of adult lifespan}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0009303 |text = rRNA transcription}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0009651 |text = response to salt stress}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0010165 |text = response to X-ray}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0010332 |text = response to gamma radiation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0010666 |text = positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0016032 |text = viral process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030154 |text = cell differentiation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030308 |text = negative regulation of cell growth}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030330 |text = DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0030512 |text = negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031065 |text = positive regulation of histone deacetylation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031497 |text = chromatin assembly}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0031571 |text = mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0032461 |text = positive regulation of protein oligomerization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0033077 |text = T cell differentiation in thymus}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0034103 |text = regulation of tissue remodeling}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0034613 |text = cellular protein localization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0034644 |text = cellular response to UV}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035264 |text = multicellular organism growth}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0035690 |text = cellular response to drug}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042149 |text = cellular response to glucose starvation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042771 |text = intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0042981 |text = regulation of apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043065 |text = positive regulation of apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043066 |text = negative regulation of apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0043525 |text = positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0045892 |text = negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0045893 |text = positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0045944 |text = positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0046677 |text = response to antibiotic}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0046902 |text = regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0048147 |text = negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0048568 |text = embryonic organ development}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0050731 |text = positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051097 |text = negative regulation of helicase activity}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051262 |text = protein tetramerization}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0051402 |text = neuron apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0070245 |text = positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071158 |text = positive regulation of cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071456 |text = cellular response to hypoxia}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071479 |text = cellular response to ionizing radiation}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0071850 |text = mitotic cell cycle arrest}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0072332 |text = intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090200 |text = positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090343 |text = positive regulation of cell aging}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090399 |text = replicative senescence}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0090403 |text = oxidative stress-induced premature senescence}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0097193 |text = intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:0097252 |text = oligodendrocyte apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:1900740 |text = positive regulation of protein insertion into mitochondrial membrane involved in apoptotic signaling pathway}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:1901525 |text = negative regulation of macromitophagy}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:1902108 |text = regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:2000378 |text = negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:2000379 |text = positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process}} {{GNF GO|id=GO:2001244 |text = positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway}} |
||
| Hs_EntrezGene = |
| Hs_EntrezGene = ۷۱۵۷ |
||
| Hs_Ensembl = ENSG00000141510 |
| Hs_Ensembl = ENSG00000141510 |
||
| Hs_RefseqmRNA = NM_000546 |
| Hs_RefseqmRNA = NM_000546 |
||
| Hs_RefseqProtein = NP_000537 |
| Hs_RefseqProtein = NP_000537 |
||
| Hs_GenLoc_db = hg19 |
| Hs_GenLoc_db = hg19 |
||
| Hs_GenLoc_chr = |
| Hs_GenLoc_chr = ۱۷ |
||
| Hs_GenLoc_start = |
| Hs_GenLoc_start = ۷۵۶۵۰۹۷ |
||
| Hs_GenLoc_end = |
| Hs_GenLoc_end = ۷۵۹۰۸۵۶ |
||
| Hs_Uniprot = P04637 |
| Hs_Uniprot = P04637 |
||
| Mm_EntrezGene = |
| Mm_EntrezGene = ۲۲۰۵۹ |
||
| Mm_Ensembl = ENSMUSG00000059552 |
| Mm_Ensembl = ENSMUSG00000059552 |
||
| Mm_RefseqmRNA = NM_001127233 |
| Mm_RefseqmRNA = NM_001127233 |
||
| Mm_RefseqProtein = NP_001120705 |
| Mm_RefseqProtein = NP_001120705 |
||
| Mm_GenLoc_db = mm10 |
| Mm_GenLoc_db = mm10 |
||
| Mm_GenLoc_chr = |
| Mm_GenLoc_chr = ۱۱ |
||
| Mm_GenLoc_start = |
| Mm_GenLoc_start = ۶۹۵۸۰۳۵۹ |
||
| Mm_GenLoc_end = |
| Mm_GenLoc_end = ۶۹۵۹۱۸۷۳ |
||
| Mm_Uniprot = P02340 |
| Mm_Uniprot = P02340 |
||
| path = |
| path = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''پروتئین تومور P53''' {{رچ}}(Tumor Protein P53)، که به این موارد هم شناخته میشود: p53، [[آنتیژن تومور]] سلولی p53 (نام [[یونیپروت|UniProt]])، '''نگهبان ژنوم'''،<ref>{{Cite journal |pmc = 5977108|year = 2018|last1 = Toufektchan|first1 = E.|title = The Guardian of the Genome Revisited: P53 Downregulates Genes Required for Telomere Maintenance, DNA Repair, and Centromere Structure|journal = Cancers|volume = 10|issue = 5|pages = 135|last2 = Toledo|first2 = F.|pmid = 29734785|doi = 10.3390/cancers10050135}}</ref> '''فسفوپروتئین p53'''، '''سرکوبگر تومور p53'''، '''آنتیژن NY-CO-13''' یا '''پروتئین مربوط-به-تبدیل 53 (TRP53)'''، هر ایزوفرمی از پروتئینهای رمز شده توسط [[ژن|ژنهایِ]] همولوگِ جاندارانِ مختلفی چون ''TP53'' (در انسان) و ''Trp53'' (در موش) میباشد. این همولوگ (که ابتدا تصور میشد تک پروتئین باشد، و هنوز هم از آن به گونه ای صحبت میشود که گویی تک پروتئین است) در [[مهرهداران]] [[جانداران چندسلولی|چندسلولی]] نقش بنیادینی دارد، به طوری که از تشکیل [[سرطان]] پیشگیری کرده و ازین رو به عنوان [[ژن سرکوبگر تومور|سرکوبگر تومور]] عمل میکند.<ref name="Surget">{{cite journal | vauthors = Surget S, Khoury MP, Bourdon JC | title = Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: a clinical perspective | journal = OncoTargets and Therapy | volume = 7 | pages = 57–68 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24379683 | pmc = 3872270 | doi = 10.2147/OTT.S53876}}</ref> از همین رو p53 را به عنوان «نگهبان ژنوم» توصیف نمودهاند، چرا که از طریق اجتناب از جهش [[ژنوم|ژنومی]] در حفظ پایداری ژنوم نقش دارد.<ref name="ISBN 0-471-33061-2">{{cite book|vauthors=Read AP, Strachan T|title=Human molecular genetics 2|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/humanmolecularge0002stra|chapter-url-access=registration|publisher=Wiley|location=New York|year=1999|isbn=978-0-471-33061-5|chapter=Chapter 18: Cancer Genetics|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/humanmolecularge0002stra}}</ref> ازین رو ''TP53''{{یاد|حالت نوشته ''ایتالیک'' را جهت نمایش ژن و تمایزش از پروتئین حاصل از آن ژن به کار میبرند.}} را به عنوان یک ژن سروبگر تومور ردهبندی نمودهاند.<ref name="pmid 6396087">{{cite journal | vauthors = Matlashewski G, Lamb P, Pim D, Peacock J, Crawford L, Benchimol S | title = Isolation and characterization of a human p53 cDNA clone: expression of the human p53 gene | journal = The EMBO Journal | volume = 3 | issue = 13 | pages = 3257–62 | date = December 1984 | pmid = 6396087 | pmc = 557846 | doi = 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02287.x}}</ref><ref name="pmid 3456488">{{cite journal | vauthors = Isobe M, Emanuel BS, Givol D, Oren M, Croce CM | title = Localization of gene for human p53 tumour antigen to band 17p13 | journal = Nature | volume = 320 | issue = 6057 | pages = 84–5 | year = 1986 | pmid = 3456488 | doi = 10.1038/320084a0 | bibcode = 1986Natur.320...84I | s2cid = 4310476}}</ref><ref name="pmid 2047879">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Bruskin A, Jarosz D, Friedman P, Prives C, Vogelstein B | title = Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein | journal = Science | volume = 252 | issue = 5013 | pages = 1708–11 | date = June 1991 | pmid = 2047879 | doi = 10.1126/science.2047879 | bibcode = 1991Sci...252.1708K | s2cid = 19647885}}</ref><ref name="pmid 3001719">{{cite journal | vauthors = McBride OW, Merry D, Givol D | title = The gene for human p53 cellular tumor antigen is located on chromosome 17 short arm (17p13) | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 83 | issue = 1 | pages = 130–4 | date = January 1986 | pmid = 3001719 | pmc = 322805 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.83.1.130 | bibcode = 1986PNAS...83..130M}}</ref><ref name="Bourdon"/> |
|||
'''ژن پی۵۳''' (p۵۳) که همچنین [[پروتئین]] پی۵۳ نیز نامیده میشود، یک [[ژن سرکوبگر غده]] است که در انسان در ژن تی پی ۵۳ روی [[کروموزوم]] ۱۷ رمزگذاری شدهاست. این ژن در جانداران چند یاختهای بسیار کارا میباشد زیرا در هماهنگی [[چرخه یاخته ای|چرخهٔ یاختهای]] و همچنین در جلوگیری از پدید آمدن [[سرطان]] بسیار کارگر میباشد.<ref name="en.wikipedia.org">http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P53</ref> |
|||
ژن پی۵۳ «پاسدار [[ژنوم]]» خوانده شدهاست چون این ژن در نگهداشت پایایی ژنوم با جلوگیری از جهش در آن نقش دارد.<ref>Read, A. P. ; Strachan, T. (1999). "Chapter 18: Cancer Genetics". Human molecular genetics 2. New York: Wiley. {{ISBN|0-471-33061-2|en}}.</ref> |
|||
نام '''p53''' در ۱۹۷۹ میلادی جهت توصیف [[جرم مولکولی]] ظاهری به کار رفت؛ تحلیل SDS-PAGE نشان میدهد که این پروتئین دارای وزن مولکولی ۵۳-[[یکای جرم اتمی|کیلودالتون]] (kDa) است. با این حال، وزن حقیقی پروتئین p53 با طول کامل، براساس جمع جرمهای ریشههای [[آمینواسید|آمینواسیدی]] تنها 43.7kDa است. این اختلاف وزن به علت تعداد بالای ریشههای [[پرولین|پرولینی]] در پروتئین است که مهاجرتش را بر روی SDS-PAGE کند کرده و ازین رو موجب سنگین تر شدن وزن ظاهری آن میگردد.<ref name="pmid 7107651">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ziemer MA, Mason A, Carlson DM | title = Cell-free translations of proline-rich protein mRNAs | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 257 | issue = 18 | pages = 11176–80 | date = September 1982 | doi = 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)33948-6 | pmid = 7107651 | url = http://www.jbc.org/content/257/18/11176.abstract | doi-access = free}}</ref> ژن ''TP53''، علاوه بر رمز کردن پروتئین با طول کامل، حداقل ۱۵ ایزوفورم پروتئینی را رمز میکند که اندازههایشان از ۳٫۵ تا ۴۳٫۷ کیلودالتون (kDa) اند. تمام این پروتئینهای p53 را '''ایزوفرمهای p53''' مینامند.<ref name="Surget"/> ژن ''TP53'' فراوانترین میزان جهش را در سرطان انسانی داراست (بیش از ۵۰ درصد)، از همین رو ژن ''TP53'' در پیشگیری از تشکیل سرطان نقش حیاتی را داراست.<ref name="Surget"/> ژن ''TP53'' پروتئینهایی متصل شونده به DNA را رمز کرده و بیان ژن را جهت پیشگیری از جهشهای ژنومی تنظیم مینماید.<ref>{{cite book |editor-last=Levine |editor-first=Arnold Jay |editor-last2=Lane |editor-first2=David P. | name-list-style = vanc |title=The p53 family | series = Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology |date=2010|publisher=Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press|location=Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.|isbn=978-0-87969-830-0}}</ref> |
|||
نام پی۵۳ به [[وزن مولکولی]] آن بر میگردد که ۵۳ هزار [[یکای جرم اتمی|دالتون]] پروتئین میباشد هر چند که بر پایهٔ برآوردها از روی ته نشست [[اسید آمینه|اسیدآمینهٔ]] آن، وزن مولکولی پی۵۳ تنها ۴۳٫۷ هزار دالتون است.<ref name="en.wikipedia.org"/> |
|||
== ارجاعات == |
|||
این ژن کارکردهای ضدسرطان گوناگونی مانند نقش در [[آپوپتوز]] (مرگ برنامهریزی شدهٔ یاخته)، پایایی ژنوم (بازدارندگی از پیدایش جهش در ژنوم)، و جلوگیری از [[رگزایی]] دارد.<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P53#Function</ref> |
|||
{{یادداشتها}} |
|||
P53 در [[تمایز سلولی]] نیز نقش دارد. مشاهده شده است که تنظیم سطح این پروتئین از طریق [[یوبیکویتین|یوبی کوئیتیناسیون]] آن توسط آنزیم E3 لیگاز ویژه [[یاخته بنیادی|سلول های بنیادی]] بنام LIN41 یا TRIM71 و در نتیجه تخریب [[پروتئازوم|پروتئازومی]] آن که به کاهش [[بیان ژن]]های هدف مانند Puma و Noxa (فاکتورهای پرو [[خزان یاختهای|آپوپتوزی]]) و Grhl3 (دخیل در تخصصی شدن و تمایز نهایی سلولهای بنیادی) منجر می شود، برای بسته شدن صحیح [[لوله عصبی]] در دوران جنینی ضروری است.<ref>{{یادکرد ژورنال|عنوان=The ubiquitin ligase LIN41/TRIM71 targets p53 to antagonize cell death and differentiation pathways during stem cell differentiation|ژورنال=Cell Death & Differentiation|ناشر=|تاریخ=2017 Jun 1|زبان=|شاپا=|doi=10.1038/cdd.2017.54|پیوند=https://www.nature.com/articles/cdd201754|تاریخ دسترسی=}}</ref> |
|||
== منابع == |
== منابع == |
||
نسخهٔ ۱ ژوئیهٔ ۲۰۲۱، ساعت ۲۱:۳۶
پروتئین تومور P53 (Tumor Protein P53)، که به این موارد هم شناخته میشود: p53، آنتیژن تومور سلولی p53 (نام UniProt)، نگهبان ژنوم،[۲] فسفوپروتئین p53، سرکوبگر تومور p53، آنتیژن NY-CO-13 یا پروتئین مربوط-به-تبدیل 53 (TRP53)، هر ایزوفرمی از پروتئینهای رمز شده توسط ژنهایِ همولوگِ جاندارانِ مختلفی چون TP53 (در انسان) و Trp53 (در موش) میباشد. این همولوگ (که ابتدا تصور میشد تک پروتئین باشد، و هنوز هم از آن به گونه ای صحبت میشود که گویی تک پروتئین است) در مهرهداران چندسلولی نقش بنیادینی دارد، به طوری که از تشکیل سرطان پیشگیری کرده و ازین رو به عنوان سرکوبگر تومور عمل میکند.[۳] از همین رو p53 را به عنوان «نگهبان ژنوم» توصیف نمودهاند، چرا که از طریق اجتناب از جهش ژنومی در حفظ پایداری ژنوم نقش دارد.[۴] ازین رو TP53[الف] را به عنوان یک ژن سروبگر تومور ردهبندی نمودهاند.[۵][۶][۷][۸][۹]
نام p53 در ۱۹۷۹ میلادی جهت توصیف جرم مولکولی ظاهری به کار رفت؛ تحلیل SDS-PAGE نشان میدهد که این پروتئین دارای وزن مولکولی ۵۳-کیلودالتون (kDa) است. با این حال، وزن حقیقی پروتئین p53 با طول کامل، براساس جمع جرمهای ریشههای آمینواسیدی تنها 43.7kDa است. این اختلاف وزن به علت تعداد بالای ریشههای پرولینی در پروتئین است که مهاجرتش را بر روی SDS-PAGE کند کرده و ازین رو موجب سنگین تر شدن وزن ظاهری آن میگردد.[۱۰] ژن TP53، علاوه بر رمز کردن پروتئین با طول کامل، حداقل ۱۵ ایزوفورم پروتئینی را رمز میکند که اندازههایشان از ۳٫۵ تا ۴۳٫۷ کیلودالتون (kDa) اند. تمام این پروتئینهای p53 را ایزوفرمهای p53 مینامند.[۳] ژن TP53 فراوانترین میزان جهش را در سرطان انسانی داراست (بیش از ۵۰ درصد)، از همین رو ژن TP53 در پیشگیری از تشکیل سرطان نقش حیاتی را داراست.[۳] ژن TP53 پروتئینهایی متصل شونده به DNA را رمز کرده و بیان ژن را جهت پیشگیری از جهشهای ژنومی تنظیم مینماید.[۱۱]
ارجاعات
- ↑ حالت نوشته ایتالیک را جهت نمایش ژن و تمایزش از پروتئین حاصل از آن ژن به کار میبرند.
منابع
- ↑ Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP (1994). "Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations". Science. 265 (5170): 346–55. doi:10.1126/science.8023157. PMID 8023157.
{{cite journal}}: نگهداری یادکرد:نامهای متعدد:فهرست نویسندگان (link) - ↑ Toufektchan, E.; Toledo, F. (2018). "The Guardian of the Genome Revisited: P53 Downregulates Genes Required for Telomere Maintenance, DNA Repair, and Centromere Structure". Cancers. 10 (5): 135. doi:10.3390/cancers10050135. PMC 5977108. PMID 29734785.
- ↑ ۳٫۰ ۳٫۱ ۳٫۲ Surget S, Khoury MP, Bourdon JC (December 2013). "Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: a clinical perspective". OncoTargets and Therapy. 7: 57–68. doi:10.2147/OTT.S53876. PMC 3872270. PMID 24379683.
- ↑ Read AP, Strachan T (1999). "Chapter 18: Cancer Genetics". Human molecular genetics 2. New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-33061-5.
- ↑ Matlashewski G, Lamb P, Pim D, Peacock J, Crawford L, Benchimol S (December 1984). "Isolation and characterization of a human p53 cDNA clone: expression of the human p53 gene". The EMBO Journal. 3 (13): 3257–62. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02287.x. PMC 557846. PMID 6396087.
- ↑ Isobe M, Emanuel BS, Givol D, Oren M, Croce CM (1986). "Localization of gene for human p53 tumour antigen to band 17p13". Nature. 320 (6057): 84–5. Bibcode:1986Natur.320...84I. doi:10.1038/320084a0. PMID 3456488. S2CID 4310476.
- ↑ Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Bruskin A, Jarosz D, Friedman P, Prives C, Vogelstein B (June 1991). "Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein". Science. 252 (5013): 1708–11. Bibcode:1991Sci...252.1708K. doi:10.1126/science.2047879. PMID 2047879. S2CID 19647885.
- ↑ McBride OW, Merry D, Givol D (January 1986). "The gene for human p53 cellular tumor antigen is located on chromosome 17 short arm (17p13)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 83 (1): 130–4. Bibcode:1986PNAS...83..130M. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.1.130. PMC 322805. PMID 3001719.
- ↑ خطای یادکرد: خطای یادکرد:برچسب
<ref> غیرمجاز؛ متنی برای یادکردهای با نامBourdonوارد نشده است. (صفحهٔ راهنما را مطالعه کنید.). - ↑ Ziemer MA, Mason A, Carlson DM (September 1982). "Cell-free translations of proline-rich protein mRNAs". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 257 (18): 11176–80. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)33948-6. PMID 7107651.
- ↑ Levine, Arnold Jay; Lane, David P., eds. (2010). The p53 family. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. ISBN 978-0-87969-830-0.