سقط جنین ناامن
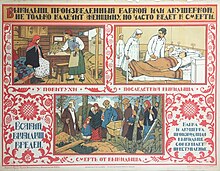
سقط جنین ناامن روش انجام عمل سقط جنین توسط افراد فاقد مهارتهای لازم یا انجام این عمل در محیطهایی با حداقل استانداردهای پزشکی یا دارا بودن هر دو این شرایط است.[۱] سقط جنین ناامن روشی خطرناک است که جان شخص را به خطر میاندازد. این روش شامل سقط جنین خود وادار کرده، سقط جنین در شرایط غیربهداشتی، و سقط جنین انجامشده توسط پزشکی است که پس از انجام آن توجه درخوری به بارور ندارد.[۲] دست کم ۲۵ میلیون سقط جنین ناامن در سال وجود دارد که اکثر آنها در کشورهای در حال توسعه رخ میدهد.[۳]
سقط جنین ناامن سالیانه منجر به ایجاد عوارض برای حدود ۷ میلیون زن میشود.[۳] سقط جنین ناامن نیز یکی از علل اصلی مرگ و میر در دوران بارداری و زایمان است (حدود ۵ تا ۱۳ درصد از کل مرگ و میرها در این دوره).[۳] اکثر سقط جنینهای ناامن در جایی اتفاق میافتند که پیشگیری از بارداری مدرن در دسترس نیست،[۴] یا در کشورهای در حال توسعه که پزشکان مقرون به صرفه و آموزشدیده به راحتی در دسترس نیستند،[۵][۶] یا جایی که سقط جنین غیرقانونی است.[۷] با محدودیتهای بیشتر طبق قانون، میزان مرگ و میر و سایر عوارض بیشتر است.[۸]
جستارهای وابسته[ویرایش]
منابع[ویرایش]
- ↑ Safe Abortion: Technical and Policy Guidance for Health Systems. World Health Organization. 2003. p. 12. ISBN 9789241590341.
a procedure for terminating an unwanted pregnancy either by persons lacking the necessary skill or in an environment lacking the minimum medical standards, or both.
- ↑ "Unsafe abortion: Global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2003" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2007. Retrieved March 7, 2011.
The estimates given in this document are intended to reflect induced abortions that carry greater risk than those carried out officially for reasons accepted in the laws of a country.
- ↑ ۳٫۰ ۳٫۱ ۳٫۲ "Preventing unsafe abortion". www.who.int (به انگلیسی). Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ↑ Singh S, Darroch JE, Ashford LS, Vlassoff M (2009). Adding it Up: The Costs and Benefits of Investing in Family Planning and Newborn Health (PDF). New York: Guttmacher Institute and United Nations Population Fund.
If women's contraceptive needs were addressed...the number of unsafe abortions would decline by 73% from 20 million to 5.5 million.
A few of the findings in that report were subsequently changed, and are available at: Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health (PDF). Guttmacher Institute. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-24. - ↑ Blas E, Kurup AS, eds. (2010). Equity, social determinants and public health programmes. World Health Organization. pp. 182–183. ISBN 9789241563970.
- ↑ Chaudhuri SK (2007). Practice Of Fertility Control: A Comprehensive Manual (7th ed.). India: Elsevier. p. 259. ISBN 9788131211502.
- ↑ Rosenthal E (October 2007). "Legal or Not, Abortion Rates Compare". New York Times. Retrieved 2009-06-30.
- ↑ Haddad LB, Nour NM (2009). "Unsafe abortion: unnecessary maternal mortality". Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2 (2): 122–126. PMC 2709326. PMID 19609407.
- مشارکتکنندگان ویکیپدیا. «Unsafe abortion». در دانشنامهٔ ویکیپدیای انگلیسی، بازبینیشده در ۲۵ ژوئن ۲۰۲۳.
برای مطالعهٔ بیشتر[ویرایش]
- حسینی، سیدمحمد؛ رهایی، سعید (۹ بهمن ۱۴۰۰). «نگاهی کارکردگرایانه به «سقط جنین آزاد» با تأکید بر رویه دیوان اروپایی حقوق بشر» (PDF). دانشگاه مفید.
- «شما؛ تجربههایی از سقط جنین ناامن در ایران و افغانستان». بیبیسی فارسی. ۱۰ ژوئن ۲۰۱۸.
