استراموستین فسفات: تفاوت میان نسخهها
محتوای حذفشده محتوای افزودهشده
قلی زادگان (بحث | مشارکتها) ایجاد شده بهواسطهٔ ترجمهٔ صفحهٔ «Estramustine phosphate» |
(بدون تفاوت)
|
نسخهٔ ۷ ژوئن ۲۰۲۱، ساعت ۱۹:۳۷
 | |
 | |
| دادههای بالینی | |
|---|---|
| نامهای تجاری | Emcyt, Estracyt |
| نامهای دیگر | EMP; Leo 299; NSC-89199; Ro 21-8837/001; Estradiol normustine phosphate; Estradiol 3-normustine 17β-phosphate; Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| مدلاین پلاس | a608046 |
| دادهها | |
| ردهبندی داروهای بارداری |
|
| روش مصرف دارو | By mouth |
| کد ATC | |
| وضعیت قانونی | |
| وضعیت قانونی |
|
| دادههای فارماکوکینتیک | |
| زیست فراهمی | 44–75% (as estramustine and estromustine)[۱] |
| پیوند پروتئینی | • Estradiol: 98%[۲] • Estrone: 96%[۲] |
| متابولیسم | Liver, intestines[۳][۱][۶] |
| متابولیتها | • Estramustine[۳][۱] • Estromustine[۳][۱] • Estradiol[۳][۱] • Estrone[۳][۱] • Phosphoric acid[۳][۱] • Normustine[۴] |
| نیمهعمر حذف | • EMP: 1.27 hours[۵] • Estromustine: 10–14 hrs[۱] • Estrone: 15–17 hours[۱] |
| دفع | Bile, feces (2.9–4.8%)[۱][۶] |
| شناسهها | |
| |
| شمارهٔ سیایاس | |
| پابکم CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| دراگبنک | |
| کماسپایدر | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.193 |
| دادههای فیزیکی و شیمیایی | |
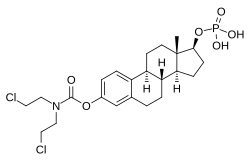
| فرمول شیمیایی | C23H32Cl2NO6P |
| جرم مولی | ۵۲۰٫۳۸ g·mol−1 |
| مدل سه بعدی (جیمول) | |
| |
| |
استراموستین فسفات (EMP)، همچنین با عنوان استرادیول نورموستین فسفات نیز شناخته شده و تحت نام های تجاری Emcyt و Estracyt فروخته می شود، یک استروژن دوگانه است که به غنوان داروی شیمی درمانی در درمان سرطان پروستات در مردان مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد.[۷][۸][۹][۱۰][۱۱][۱۲][۱۳][۱۴][۱۵][۱۶]
این دارو چند بار در روز به شکل خوراکی یا به صورت تزریق داخل وریدی تجویز می شود.[۱۷][۱۸][۱۹][۲۰][۲۱][۲۲]
EMP برای استفاده پزشکی در اوایل دهه 1970 معرفی شد.[۳] در ایالات متحده، کانادا، انگلستان، سایر کشورهای اروپایی و سایر نقاط جهان در دسترس است.[۲۳][۲۴]

منابع
مطالعه بیشتر
- Tew KD (September 1983). "The mechanism of action of estramustine". Semin. Oncol. 10 (3 Suppl 3): 21–6. PMID 6364362.
- Hoisaeter PA, Bakke A (September 1983). "Estramustine phosphate (Estracyt): experimental and clinical studies in Europe". Semin. Oncol. 10 (3 Suppl 3): 27–33. PMID 6364363.
- Sandberg AA (September 1983). "Metabolic aspects and actions unique to Estracyt". Semin. Oncol. 10 (3 Suppl 3): 3–15. PMID 6364364.
- Haukaas SA (1984). "Immunological effects of diethylstilbestrol and estramustine phosphate". Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 83: 1–32. PMID 6387896.
- Hauser AR, Merryman R (May 1984). "Estramustine phosphate sodium". Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 18 (5): 368–74. doi:10.1177/106002808401800502. PMID 6373212. S2CID 25303747.
- Sandberg AA (June 1984). "Metabolic parameters of Estracyt pertinent to its effects in prostatic cancer". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 11–21. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80092-8. PMID 6375075.
- Gunnarsson PO, Forshell GP (June 1984). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of estramustine phosphate". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 22–7. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80093-X. PMID 6375076.
- Forsgren B, Björk P (June 1984). "Specific binding of estramustine to prostatic proteins". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 34–8. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80095-3. PMID 6375077.
- Kalland T, Haukaas SA (June 1984). "Immunologic effects of estramustine phosphate". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 39–45. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80096-5. PMID 6375078.
- Høisaeter PA (June 1984). "Mode of action of Emcyt". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 46–8. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80097-7. PMID 6375079.
- Müntzing J, Gunnarsson K (June 1984). "Preclinical pharmacology and toxicology of estramustine phosphate". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 6–10. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80091-6. PMID 6375082.
- Slack NH, Murphy GP (June 1984). "Clinical toxicity and long-term results of Emcyt therapy for prostate cancer". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 73–7. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80103-X. PMID 6375085.
- Hedlund PO (1985). "Mode of action of estramustine phosphate in hormone dependent and hormone non-dependent prostate cancer". Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 185A: 197–202. PMID 3898129.
- Hedlund PO (1987). "Estracyt--mode of action and clinical experience". Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 243B: 215–9. PMID 3309981.
- Murphy GP (1987). "A current review of the clinical experience with Estracyt". Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 243B: 221–5. PMID 3309982.
- Forsgren B (1988). "Estramustine-binding protein in rat and human prostate". Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 107: 56–8. PMID 3287598.
- Tew KD, Stearns ME (1989). "Intracellular effects of estramustine (Estracyt/Emcyt)". Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 303: 169–75. PMID 2674983.
- Tew KD, Stearns ME (1989). "Estramustine--a nitrogen mustard/steroid with antimicrotubule activity". Pharmacol. Ther. 43 (3): 299–319. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(89)90012-0. PMID 2682681.
- Könyves I (1989). "Estramustine phosphate (Estracyt) in the treatment of prostatic carcinoma". Int Urol Nephrol. 21 (4): 393–7. doi:10.1007/BF02559635. PMID 2693392.
- Benson R, Hartley-Asp B (1990). "Mechanisms of action and clinical uses of estramustine". Cancer Invest. 8 (3–4): 375–80. doi:10.3109/07357909009012056. PMID 2207764.
- Van Poppel H, Baert L (1991). "The present role of estramustine phosphate in advanced prostate cancer". Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 370: 323–41. PMID 1924466.
- Janknegt RA (1992). "Estramustine phosphate and other cytotoxic drugs in the treatment of poor prognostic advanced prostate cancer". Prostate Suppl. 4: 105–10. doi:10.1002/pros.2990210516. PMID 1574449. S2CID 40562112.
- Tew KD, Glusker JP, Hartley-Asp B, Hudes G, Speicher LA (December 1992). "Preclinical and clinical perspectives on the use of estramustine as an antimitotic drug". Pharmacol. Ther. 56 (3): 323–39. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(92)90023-S. PMID 1301594.
- Kreis W (1995). "Estramustine revisited". Cancer Treat. Res. Cancer Treatment and Research. 78: 163–84. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-2007-8_8. ISBN 978-1-4613-5829-9. PMID 8595142.
- Perry CM, McTavish D (July 1995). "Estramustine phosphate sodium. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in prostate cancer". Drugs Aging. 7 (1): 49–74. doi:10.2165/00002512-199507010-00006. PMID 7579781.
- Hudes G (February 1997). "Estramustine-based chemotherapy". Semin. Urol. Oncol. 15 (1): 13–9. PMID 9050135.
- Bergenheim AT, Henriksson R (February 1998). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of estramustine phosphate". Clin Pharmacokinet. 34 (2): 163–72. doi:10.2165/00003088-199834020-00004. PMID 9515186.
- Kitamura T (February 2001). "Necessity of re-evaluation of estramustine phosphate sodium (EMP) as a treatment option for first-line monotherapy in advanced prostate cancer". Int. J. Urol. 8 (2): 33–6. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2001.00254.x. PMID 11240822.
- Simpson, D; Wagstaff, AJ (2003). "Estramustine Phosphate Sodium". American Journal of Cancer. 2 (5): 373–390. doi:10.2165/00024669-200302050-00013. S2CID 70507026.
- Ravery V, Fizazi K, Oudard S, Drouet L, Eymard JC, Culine S, Gravis G, Hennequin C, Zerbib M (December 2011). "The use of estramustine phosphate in the modern management of advanced prostate cancer". BJU Int. 108 (11): 1782–6. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10201.x. PMID 21756277.
- Qin Z, Li X, Zhang J, Tang J, Han P, Xu Z, Yu Y, Yang C, Wang C, Xu T, Xu Z, Zou Q (September 2016). "Chemotherapy with or without estramustine for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Medicine (Baltimore). 95 (39): e4801. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004801. PMC 5265899. PMID 27684806.
- Inoue, Takahiro (2018). "Role of Estramustine Phosphate and Other Estrogens for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer". Hormone Therapy and Castration Resistance of Prostate Cancer. pp. 249–256. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-7013-6_26. ISBN 978-981-10-7012-9.
- ↑ ۱٫۰۰ ۱٫۰۱ ۱٫۰۲ ۱٫۰۳ ۱٫۰۴ ۱٫۰۵ ۱٫۰۶ ۱٫۰۷ ۱٫۰۸ ۱٫۰۹ ۱٫۱۰ Bergenheim AT, Henriksson R (February 1998). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of estramustine phosphate". Clin Pharmacokinet. 34 (2): 163–72. doi:10.2165/00003088-199834020-00004. PMID 9515186.
- ↑ ۲٫۰ ۲٫۱ خطای یادکرد: خطای یادکرد:برچسب
<ref> غیرمجاز؛ متنی برای یادکردهای با نامpmid16112947وارد نشده است. (صفحهٔ راهنما را مطالعه کنید.). - ↑ ۳٫۰ ۳٫۱ ۳٫۲ ۳٫۳ ۳٫۴ ۳٫۵ ۳٫۶ Kitamura T (February 2001). "Necessity of re-evaluation of estramustine phosphate sodium (EMP) as a treatment option for first-line monotherapy in advanced prostate cancer". Int. J. Urol. 8 (2): 33–6. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2001.00254.x. PMID 11240822.
- ↑ خطای یادکرد: خطای یادکرد:برچسب
<ref> غیرمجاز؛ متنی برای یادکردهای با نامInoue2018وارد نشده است. (صفحهٔ راهنما را مطالعه کنید.). - ↑ ۵٫۰ ۵٫۱ Perry CM, McTavish D (July 1995). "Estramustine phosphate sodium. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in prostate cancer". Drugs Aging. 7 (1): 49–74. doi:10.2165/00002512-199507010-00006. PMID 7579781.
- ↑ ۶٫۰ ۶٫۱ "Emcyt (estramustine) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ↑ https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/018045s023lbl.pdf
- ↑ Inoue, Takahiro (2018). "Role of Estramustine Phosphate and Other Estrogens for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer". Hormone Therapy and Castration Resistance of Prostate Cancer. pp. 249–256. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-7013-6_26. ISBN 978-981-10-7012-9.
- ↑ Qin Z, Li X, Zhang J, Tang J, Han P, Xu Z, Yu Y, Yang C, Wang C, Xu T, Xu Z, Zou Q (September 2016). "Chemotherapy with or without estramustine for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Medicine (Baltimore). 95 (39): e4801. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004801. PMC 5265899. PMID 27684806.
- ↑ Ravery V, Fizazi K, Oudard S, Drouet L, Eymard JC, Culine S, Gravis G, Hennequin C, Zerbib M (December 2011). "The use of estramustine phosphate in the modern management of advanced prostate cancer". BJU Int. 108 (11): 1782–6. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10201.x. PMID 21756277.
- ↑ Simpson, D; Wagstaff, AJ (2003). "Estramustine Phosphate Sodium". American Journal of Cancer. 2 (5): 373–390. doi:10.2165/00024669-200302050-00013. S2CID 70507026.
- ↑ Kitamura T (February 2001). "Necessity of re-evaluation of estramustine phosphate sodium (EMP) as a treatment option for first-line monotherapy in advanced prostate cancer". Int. J. Urol. 8 (2): 33–6. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2001.00254.x. PMID 11240822.
- ↑ Bergenheim AT, Henriksson R (February 1998). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of estramustine phosphate". Clin Pharmacokinet. 34 (2): 163–72. doi:10.2165/00003088-199834020-00004. PMID 9515186.
- ↑ Hudes G (February 1997). "Estramustine-based chemotherapy". Semin. Urol. Oncol. 15 (1): 13–9. PMID 9050135.
- ↑ Perry CM, McTavish D (July 1995). "Estramustine phosphate sodium. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in prostate cancer". Drugs Aging. 7 (1): 49–74. doi:10.2165/00002512-199507010-00006. PMID 7579781.
- ↑ Kreis W (1995). "Estramustine revisited". Cancer Treat. Res. Cancer Treatment and Research. 78: 163–84. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-2007-8_8. ISBN 978-1-4613-5829-9. PMID 8595142.
- ↑ https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/018045s023lbl.pdf
- ↑ Qin Z, Li X, Zhang J, Tang J, Han P, Xu Z, Yu Y, Yang C, Wang C, Xu T, Xu Z, Zou Q (September 2016). "Chemotherapy with or without estramustine for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Medicine (Baltimore). 95 (39): e4801. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004801. PMC 5265899. PMID 27684806.
- ↑ Kitamura T (February 2001). "Necessity of re-evaluation of estramustine phosphate sodium (EMP) as a treatment option for first-line monotherapy in advanced prostate cancer". Int. J. Urol. 8 (2): 33–6. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2001.00254.x. PMID 11240822.
- ↑ Bergenheim AT, Henriksson R (February 1998). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of estramustine phosphate". Clin Pharmacokinet. 34 (2): 163–72. doi:10.2165/00003088-199834020-00004. PMID 9515186.
- ↑ Perry CM, McTavish D (July 1995). "Estramustine phosphate sodium. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in prostate cancer". Drugs Aging. 7 (1): 49–74. doi:10.2165/00002512-199507010-00006. PMID 7579781.
- ↑ Kreis W (1995). "Estramustine revisited". Cancer Treat. Res. Cancer Treatment and Research. 78: 163–84. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-2007-8_8. ISBN 978-1-4613-5829-9. PMID 8595142.
- ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 406–407. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/international/estramustine.html
- ↑ Gunnarsson PO, Forshell GP (June 1984). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of estramustine phosphate". Urology. 23 (6 Suppl): 22–7. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(84)80093-X. PMID 6375076.
- ↑ Ozeki T, Takeuchi M, Suzuki M, Kitamura T, Takayanagi R, Yokoyama H, Yamada Y (October 2009). "Single nucleotide polymorphisms of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 7 gene: mechanism of estramustine-related adverse reactions?". Int. J. Urol. 16 (10): 836–41. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2009.02374.x. PMID 19735314.
- ↑ Suzuki M, Muto S, Hara K, Ozeki T, Yamada Y, Kadowaki T, Tomita K, Kameyama S, Kitamura T (February 2005). "Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase genes might predict the risk of side-effects of estramustine phosphate sodium in prostate cancer patients". Int. J. Urol. 12 (2): 166–72. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2005.01004.x. PMID 15733111.
