پیرابین
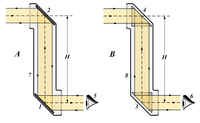
A - Periscope using two plane mirrors.
B - Periscope using two right–angled prisms.
1 - 2 - Plane mirrors.
3 - 4 - Right–angled prisms.
5 - 6 - Observer eye.
7 - 8 - Periscope tube.
H - Periscope optical height.


۱ - Eyepiece
۲ - Diagonal prism
۳ - Handle
۴–۶ - Erecting lenses
۵ - Periscope tube
۷ - Field lens
۸ - Lens
۹ - Head diagonal prism
۱۰ - Window
پیرابین یا پریسکوپ (به فرانسوی: Périscope) ابزاری است برای دیدن اشیائی که بالاتر از سطح چشم بینندهاند (برای نمونه در زیردریایی) یا بگونهای قرار دارند که دیدن مستقیم آنها میسر نیست. این ابزار تشکیل یافتهاست از یک لوله دراز، که در هر یک از دو سر آن منشوری راستگوشه چنان قرار داده شدهاست که نور در اثر تابش کلی درونی از روی وجه بزرگتر آنها با زاویه ۹۰c در هر منشور منحرف میشود، بنابراین نور از شیئی مورد نظر در راستای موازی با راستای اولیه (تابش از) شیئی ولی پائینتر وارد چشم ناظر میشود.[۱][۲]
پیرابین در امور نظامی مانند دیدهبانی و همچنین در زیردریاییها، خودروهای زرهی و تانکها نیز بهکار میرود. این وسیله برای اولین بار در سال ۱۹۰۲ توسط سایمون لیک اختراع شدهاست.
جستارهای وابسته[ویرایش]
منابع[ویرایش]
- ↑ Walker, Bruce H. (2000). Optical Design for Visual Systems. SPIE Press. p. 117. ISBN 978-0-8194-3886-7.
- ↑ The Submarine Periscope: An Explanation of the Principles Involved in Its Construction, Together with a Description of the Main Features of the Barr and Stroud Periscopes. Barr and Stroud Limited. 1928.
- فرهنگستان زبان و ادب فارسی
| در ویکیانبار پروندههایی دربارهٔ پیرابین موجود است. |
