پرونده:SG RLS LMS chan var.png
محتوای صفحه در زبانهای دیگر پشتیبانی نمیشود
ظاهر
از ویکیپدیا، دانشنامهٔ آزاد
SG_RLS_LMS_chan_var.png (۵۶۱ × ۴۲۰ پیکسل، اندازهٔ پرونده: ۱۲ کیلوبایت، نوع MIME پرونده: image/png)
این پرونده در ویکیانبار موجود است. محتویات صفحهٔ توصیف آن در زیر نمایش داده میشود. |
خلاصه
| توضیحSG RLS LMS chan var.png |
English: Developed according to TU Ilmenau teaching materials.
clear all; close all; clc
%% Initialization
% channel parameters
sigmaS = 1; %signal power
sigmaN = 0.01; %noise power
% CSI (channel state information):
% the channel for the transmission of the first NS1 training symbols
channel1 = [0.722 - 0.779i; -0.257 - 0.722i; -0.789 - 1.862i];
% the channel for the transmission of the next NS2 training symbols
channel2 = [-0.831 - 0.661i;-1.071 - 0.961i; -0.551 - 0.311i];
M = 5; % filter order
% step sizes
mu_LMS = [0.01,0.07];
mu_SG = [0.01,0.07];
% symbols / ensembles
NS1 = 500;
NS2 = 500;
NS = NS1+NS2;
NEnsembles = 1000; %number of ensembles
%% Compute Rxx and p
%the maximum index of channel taps (l=0,1...L):
L = length(channel1) - 1;
H = convmtx(channel1, M-L); %channel matrix (Toeplitz structure)
Rnn = sigmaN*eye(M); %the noise covariance matrix
% Inline functions:
calc_Rxx = @(channel) ...
sigmaS*(convmtx(channel, M-L)*convmtx(channel, M-L)')+sigmaN*eye(M);
calc_p = @(channel) sigmaS*(convmtx(channel,M-L))*[1; zeros(M-L-1, 1)];
Rxx = zeros(M,M,2);
p = zeros(M,2);
A = calc_Rxx(channel1);
Rxx(:,:,1) = calc_Rxx(channel1);
Rxx(:,:,2) = calc_Rxx(channel2);
p(:,1) = calc_p(channel1);
p(:,2) = calc_p(channel2);
% An inline function to calculate MSE(w) for a weight vector w
calc_MSE = @(w, ch) real(w'*Rxx(:,:,ch)*w - w'*p(:, ch) - p(:, ch)'*w + sigmaS);
%% Adaptive Equalization
N_test = 2;
MSE_LMS = zeros(NEnsembles, NS, N_test);
MSE_SG = zeros(NEnsembles, NS, N_test);
MSE_RLS = zeros(NEnsembles, NS, N_test);
for nEnsemble = 1:NEnsembles
%initial symbols:
symbols1 = sigmaS*sign(randn(1,NS1));
symbols2 = sigmaS*sign(randn(1,NS2));
%received noisy symbols:
X1 = convmtx(channel1, M-L)*hankel(symbols1(1:M-L),[symbols1(M-L:end),zeros(1,M-L-1)]) + ...
sqrt(sigmaN)*(randn(M,NS1)+1j*randn(M,NS1))/sqrt(2);
X2 = convmtx(channel2, M-L)*hankel(symbols2(1:M-L),[symbols2(M-L:end),zeros(1,M-L-1)]) + ...
sqrt(sigmaN)*(randn(M,NS2)+1j*randn(M,NS2))/sqrt(2);
X = [X1, X2];
symbols = [symbols1, symbols2];
for n_mu = 1:N_test
w_LMS = zeros(M,1);
w_SG = zeros(M,1);
p_SG = zeros(M,1);
R_SG = zeros(M);
for n = 1:NS
if n <= NS1, curh = 1; else curh = 2; end
%% LMS - Least Mean Square
e = symbols(n) - w_LMS'*X(:,n);
w_LMS = w_LMS + mu_LMS(n_mu)*X(:,n)*conj(e);
MSE_LMS(nEnsemble,n,n_mu)= calc_MSE(w_LMS, curh);
%% SG - Stochastic gradient
R_SG = 1/n*((n-1)*R_SG + X(:,n)*X(:,n)');
p_SG = 1/n*((n-1)*p_SG + X(:,n)*conj(symbols(n)));
w_SG = w_SG + mu_SG(n_mu)*(p_SG - R_SG*w_SG);
MSE_SG(nEnsemble,n,n_mu)= calc_MSE(w_SG, curh);
end
end
%RLS - Recursive Least Squares
lambda_RLS = [0.8; 1]; %forgetting factors
for n_lambda=1:length(lambda_RLS)
%Initialize the weight vectors for RLS
delta = 1;
w_RLS = zeros(M,1);
P = eye(M)/delta; % (n-1)-th iteration, where n = 1,2...
PI = zeros(M,1); % n-th iteration
K = zeros(M,1);
for n=1:NS
if n <= NS1, curh = 1; else curh = 2; end
% the recursive process of RLS
PI = P*X(:,n);
K = PI/(lambda_RLS(n_lambda)+X(:,n)'*PI);
ee = symbols(n) - w_RLS'*X(:,n);
w_RLS = w_RLS + K*conj(ee);
MSE_RLS(nEnsemble,n,n_lambda)= calc_MSE(w_RLS, curh);
P = P/lambda_RLS(n_lambda) - K/lambda_RLS(n_lambda)*X(:,n)'*P;
end
end
end
%% Wiener Solution
MSE_Wiener(1:NS1) = calc_MSE(Rxx(:,:,1)\p(:,1),1);
MSE_Wiener(NS1+1:NS) = calc_MSE(Rxx(:,:,2)\p(:,2),2);
MSE_LMS_1 = mean(MSE_LMS(:,:,1));
MSE_LMS_2 = mean(MSE_LMS(:,:,2));
MSE_SG_1 = mean(MSE_SG(:,:,1));
MSE_SG_2 = mean(MSE_SG(:,:,2));
MSE_RLS_1 = mean(MSE_RLS(:,:,1));
MSE_RLS_2 = mean(MSE_RLS(:,:,2));
figure(1)
n = 1:NS;
m= [2 4 6 10 30 60 100 300 600 1000];
semilogy(m, MSE_LMS_1(m),'+','linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
hold all;
semilogy(m, MSE_LMS_2(m),'o','linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
semilogy(m, MSE_SG_1(m),'+','linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(m, MSE_SG_2(m),'o','linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(m, MSE_RLS_1(m),'+','linewidth',2, 'color','green');
semilogy(m, MSE_RLS_2(m),'o','linewidth',2, 'color','green');
semilogy(n, MSE_Wiener(n), 'color','black','linewidth',2);
semilogy(n, MSE_LMS_1(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
semilogy(n, MSE_LMS_2(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
semilogy(n, MSE_SG_1(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(n, MSE_SG_2(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(n, MSE_RLS_1(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','green');
semilogy(n, MSE_RLS_2(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','green');
grid on
xlabel('Ns');
ylabel('MSE');
title(['LMS, SG, RLS, \sigma_N= ' num2str(sigmaN) ', \sigma_S= '...
num2str(sigmaS) ', M= ' num2str(M) ', L= ' num2str(L) ]);
legend(['LMS, \mu=' num2str(mu_LMS(1))],['LMS, \mu=' num2str(mu_LMS(2))],...
['SG, \mu=' num2str(mu_SG(1))],['SG, \mu=' num2str(mu_SG(2))],...
['RLS, \lambda=' num2str(lambda_RLS(1))],['RLS, \lambda=' ...
num2str(lambda_RLS(2))],'Weiner solution',2);
axis([0 NS 0.002 1])
|
| تاریخ | |
| منبع | اثر شخصی |
| پدیدآور | Kirlf |
اجازهنامه
من، صاحب حقوق قانونی این اثر، به این وسیله این اثر را تحث اجازهنامهٔ ذیل منتشر میکنم:
این پرونده تحت پروانهٔ Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International منتشر شده است.
- شما اجازه دارید:
- برای به اشتراک گذاشتن – برای کپی، توزیع و انتقال اثر
- تلفیق کردن – برای انطباق اثر
- تحت شرایط زیر:
- انتساب – شما باید اعتبار مربوطه را به دست آورید، پیوندی به مجوز ارائه دهید و نشان دهید که آیا تغییرات ایجاد شدهاند یا خیر. شما ممکن است این کار را به هر روش منطقی انجام دهید، اما نه به هر شیوهای که پیشنهاد میکند که مجوزدهنده از شما یا استفادهتان حمایت کند.
- انتشار مشابه – اگر این اثر را تلفیق یا تبدیل میکنید، یا بر پایه آن اثری دیگر خلق میکنید، میبایست مشارکتهای خود را تحت مجوز یکسان یا مشابه با ا اصل آن توزیع کنید.
عنوان
شرحی یکخطی از محتوای این فایل اضافه کنید
The mean square error perofrmance of Least mean squares filter, Stochastic gradient descent and Recursive least squares filter in dependance of training symbols in case of changed during the training procedure channel.
آیتمهایی که در این پرونده نمایش داده شدهاند
توصیفها
این خصوصیت مقداری دارد اما نامشخص است.
source of file انگلیسی
original creation by uploader انگلیسی
۲ مارس 2019
image/png
تاریخچهٔ پرونده
روی تاریخ/زمانها کلیک کنید تا نسخهٔ مربوط به آن هنگام را ببینید.
| تاریخ/زمان | بندانگشتی | ابعاد | کاربر | توضیح | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| کنونی | ۱۵ ژوئیهٔ ۲۰۱۹، ساعت ۱۹:۰۵ | 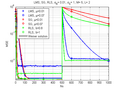 | ۵۶۱ در ۴۲۰ (۱۲ کیلوبایت) | Kirlf | Noise power are fixed in the signal model. |
| ۲ مارس ۲۰۱۹، ساعت ۱۶:۲۴ |  | ۵۶۱ در ۴۲۰ (۱۲ کیلوبایت) | Kirlf | User created page with UploadWizard |
کاربرد پرونده
صفحهٔ زیر از این تصویر استفاده میکند:
کاربرد سراسری پرونده
ویکیهای دیگر زیر از این پرونده استفاده میکنند:
- کاربرد در en.wikipedia.org
فراداده
این پرونده حاوی اطلاعات اضافهای است که احتمالاً دوربین دیجیتال یا پویشگری که در ایجاد یا دیجیتالی کردن آن به کار رفته آن را افزوده است. اگر پرونده از وضعیت ابتداییاش تغییر داده شده باشد آنگاه ممکن است شرح و تفصیلات موجود اطلاعات تصویر را تماماً بازتاب ندهد.
| تفکیکپذیری افقی | ۳۷٫۸ نقطه در سانتیمتر |
|---|---|
| تفکیکپذیری عمودی | ۳۷٫۸ نقطه در سانتیمتر |
| تاریخ و زمان تغییر پرونده | ۱۵ ژوئیهٔ ۲۰۱۹، ساعت ۱۹:۰۲ |
| نرمافزار استفادهشده |
|
| تاریخ و زمان دیجیتالیشدن |
|

