پرونده:Lens and wavefronts.gif
Lens_and_wavefronts.gif (۱۸۳ × ۳۵۶ پیکسل، اندازهٔ پرونده: ۳۵ کیلوبایت، نوع MIME پرونده: image/gif، چرخشدار، ۹ قاب، ۰٫۷ ثانیه)
تاریخچهٔ پرونده
روی تاریخ/زمانها کلیک کنید تا نسخهٔ مربوط به آن هنگام را ببینید.
| تاریخ/زمان | بندانگشتی | ابعاد | کاربر | توضیح | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| کنونی | ۲۵ نوامبر ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۶:۳۵ |  | ۱۸۳ در ۳۵۶ (۳۵ کیلوبایت) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak |
| ۲۴ نوامبر ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۴:۱۰ |  | ۱۷۱ در ۳۵۶ (۳۳ کیلوبایت) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak | |
| ۲۴ نوامبر ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۴:۰۹ |  | ۱۷۱ در ۳۵۶ (۳۳ کیلوبایت) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak | |
| ۲۴ نوامبر ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۰:۵۶ |  | ۱۷۱ در ۳۵۹ (۳۳ کیلوبایت) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak, same license | |
| ۲۴ نوامبر ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۰:۵۳ | 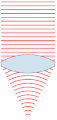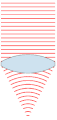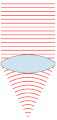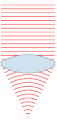 | ۱۷۱ در ۳۵۹ (۳۲ کیلوبایت) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak | |
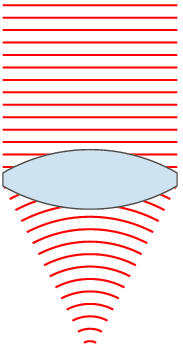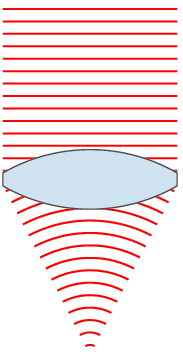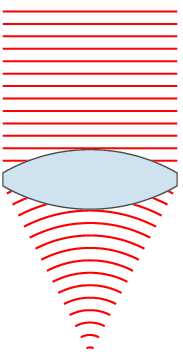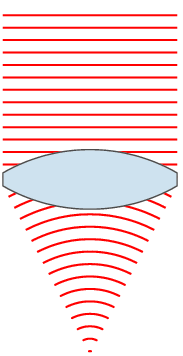
| ۲۴ نوامبر ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۰:۴۹ |  | ۱۵۱ در ۳۵۹ (۳۱ کیلوبایت) | Oleg Alexandrov | {{Information |Description=Illustration of wavefronts after passing through a [:en:lens (optics)|lens]] |Source=self-made with MATLAB |Date=~~~~~ |Author= Oleg Alexandrov |Permission=see below |other_versions= }} |
کاربرد پرونده
صفحهٔ زیر از این تصویر استفاده میکند:
کاربرد سراسری پرونده
ویکیهای دیگر زیر از این پرونده استفاده میکنند:
- کاربرد در ar.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در ast.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در be.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در bn.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در bs.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در ckb.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در cs.wikiversity.org
- کاربرد در cv.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در en.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در en.wikiversity.org
- کاربرد در es.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در es.wikiversity.org
- کاربرد در eu.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در fi.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در fr.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در fr.wikibooks.org
- کاربرد در fy.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در ga.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در he.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در hi.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در hr.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در hy.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در id.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در lt.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در lv.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در ml.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در mn.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در nl.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در pa.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در ru.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در sh.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در si.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در sl.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در sr.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در sv.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در ta.wikipedia.org
نمایش استفادههای سراسری از این پرونده.