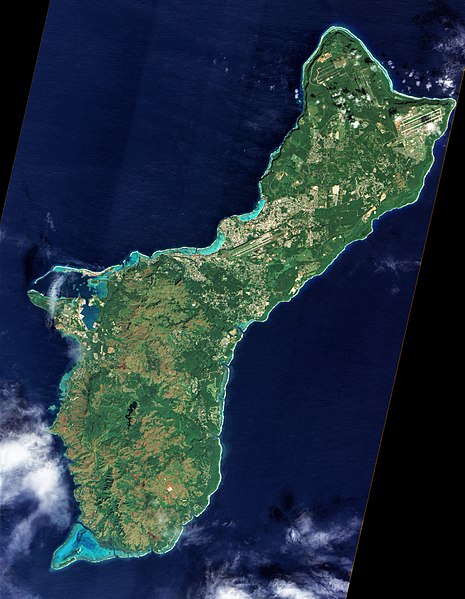
English: On December 30, 2011, cloud-free skies presented NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite with this unobstructed view of the island of Guam. Note that this image, taken by the satellite’s Advanced Land Imager (ALI), has been rotated and north is at right.
Located in the tropical Pacific Ocean, the U.S. territory of Guam lies at the southern end of the Mariana Island Chain. As the largest island in that archipelago, Guam stretches roughly 30 miles (50 kilometers) from northeast to southwest. Fields, forests, military bases, and settlements all mix on the landscape. Two prominent airstrips run northeast-southwest, one at the northeastern tip of the island, and the other in central Guam.
Guam has two seasons: wet (June to December) and dry (January to June), and ALI acquired this image during the transition from wet to dry. The fate of that rainwater has a lot to do with whether it lands in the northern or southern part of the island. In southern Guam, volcanic rock predominates, but in northern Guam, limestone overlies volcanic rock. Limestone is porous—so porous, in fact, that practically all the water in northern Guam infiltrates the rock. After percolating through the limestone, water in northern Guam becomes part of the groundwater system. Guam’s rivers are confined to the southern part of the island, where less porous volcanic rock enables water to collect on the surface.
Coral reefs fringe the island, and they are especially visible around Apra Harbor and Cocos Lagoon. Shallow water along these reefs glows peacock blue.
Not far from Guam, the ocean is anything but shallow. Just east of the Mariana Islands lies the Mariana Trench. Located at the boundary between tectonic plates, it is the deepest point in the Earth’s ocean.
References
- CIA World Factbook. (2011, November 17). Guam. Accessed February 16, 2012.
- Gingerich, S.B. (2003). Hydrologic Resources of Guam. U.S. Geological Survey. Accessed February 16, 2012.
- Guam-OnLine. (2001). Map of Guam. Accessed February 16, 2012.
- Siegrist, H.G., Reagan, M.K., Randall, R.H., Jenson, J.W. (2007). Geologic Map and Sections of Guam, Mariana Islands. (PDF file, 6 MB). Accessed February 16, 2012.
NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team and the United States Geological Survey. Caption by Michon Scott.
Instrument:
EO-1 - ALI